Python3 conditional control
Python 3 Conditional Control
Python Conditional statements determine the execution of a block of code based on the results (True or False) of one or more statements.
Code Execution Process:
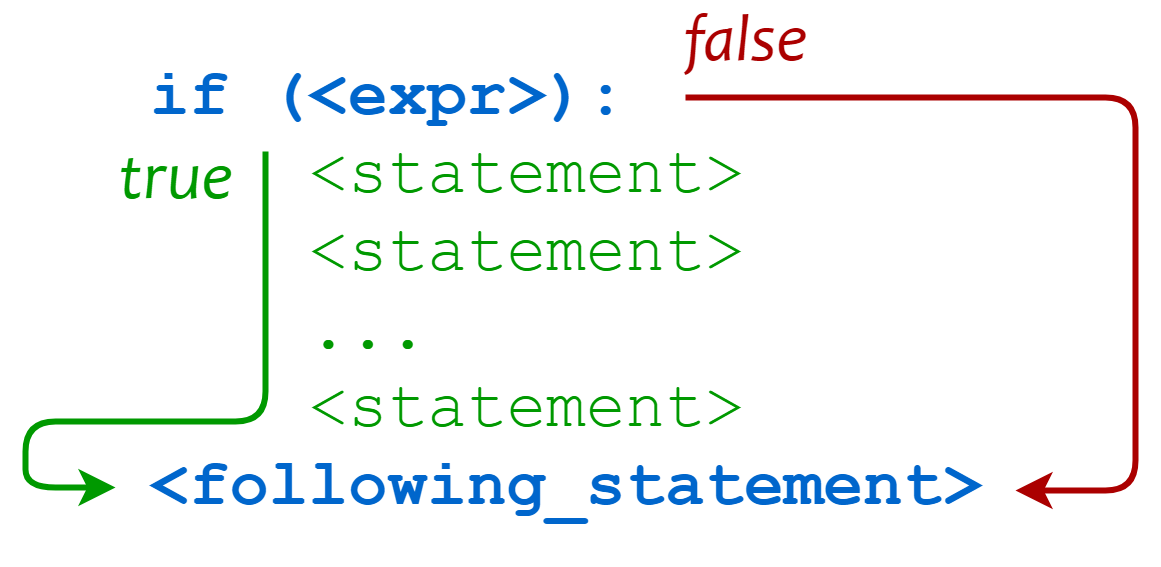
if Statement
The general form of the if statement in Python is as follows:
if condition_1:
statement_block_1
elif condition_2:
statement_block_2
else:
statement_block_3
- If “condition_1” is True, the statements in “statement_block_1” will be executed.
- If “condition_1” is False, “condition_2” will be evaluated.
- If “condition_2” is True, the statements in “statement_block_2” block statement
- If “condition_2” is False, “statement_block_3” block statement will be executed
Python uses elif instead of else if, so the keywords for an if statement are: if – elif – else.
Note:
- 1. Use a colon (:) after each condition to indicate that the following block of statements will be executed if the condition is met.
- 2. Use indentation to demarcate statement blocks. Statements with the same number of indents form a single statement block.
- 3. Python does not have a switch-case statement.
Gif Demo:

Example
The following is a simple if example:
Example
#!/usr/bin/python3
var1 = 100
if var1:
print ("1 - if expression condition is true")
print (var1)
var2 = 0
if var2:
print ("2 - if expression condition is true")
print (var2)
print ("Good bye!")
Executing the above code produces the following output:
1 - if expression condition is true
100
Good bye!
From the output, you can see that because variable var2 is 0, the corresponding if statement is not executed.
The following example demonstrates how to calculate a dog’s age:
Example
#!/usr/bin/python3
age = int(input("Please enter your dog's age: "))
print("")
if age <= 0:
print("Are you kidding me?")
elif age == 1:
print("Equivalent to a 14-year-old human.")
elif age == 2:
print("Equivalent to a 22-year-old human.")
elif age > 2:
human = 22 + (age -2)*5
print("Equivalent human age: ", human)
### Exit prompt
input("Press enter to exit")
Save the above script in the file dog.py and execute it:
$ python3 dog.py
Please enter your dog's age: 1
Equivalent to a 14-year-old person.
Press enter to exit.
The following are commonly used operators in if:
| Operator | Description | |
|---|---|---|
< |
Less than | |
<= |
Less than or equal to | |
> |
Greater than = | Greater than or equal to |
== |
Equal to, compares two values for equality | |
!= |
Not equal to |
Example
#!/usr/bin/python3
# Program demonstrates the == operator
# Using numbers
print(5 == 6)
# Using variables
x = 5
y = 8
print(x == y)
The above example outputs:
False
False
The high_low.py file demonstrates number comparison operations:
Example
#!/usr/bin/python3
# This example demonstrates a number guessing game
number = 7
guess = -1
print("Number guessing game!")
while guess != number:
guess = int(input("Please enter your guess number:"))
if guess == number:
print("Congratulations, you guessed it right!")
elif guess < number:
print("You guessed too low...")
elif guess > number:
print("You guessed too high...")
Executing the above script will produce the following output:
$ python3 high_low.py
Number Guessing Game!
Please enter your guess: 1
You guessed too low...
Please enter your guess: 9
You guessed too high...
Please enter your guess: 7
Congratulations, you guessed it right!
Nested if statements
In nested if statements, you can place an if…elif…else structure within another if…elif…else structure.
if expression 1:
Statement
if expression 2:
Statement
elif expression 3:
Statement
else:
Statement
elif expression 4:
Statement
else:
Statement
Example
# !/usr/bin/python3
num=int(input("Enter a number:"))
if num%2==0:
if num%3==0:
print ("The number you entered is divisible by 2 and 3")
else:
print ("The number you entered is divisible by 2, but not by 3")
else:
if num%3==0:
print ("The number you entered is divisible by 3, but not by 2")
else:
print ("The number you entered is not divisible by 2 and 3")
Save the above program in the test_if.py file and execute it to get the following output:
$ python3 test.py
Enter a number: 6
The number you enter is divisible by 2 and 3