Beautiful Soup – Installation
Beautiful Soup – Installation
Since Beautiful Soup isn’t a standard Python library, we need to install it first. We will install the latest Beautiful Soup 4 library (also known as BS4).
To isolate our workspace so as not to interfere with our existing setup, let’s first create a virtual environment.
Creating a Virtual Environment (Optional)
A virtual environment allows us to create an isolated Python working copy for a specific project without affecting our external setup.
The best way to install any Python package is using pip. However, if pip isn’t already installed (you can check this by using “pip -version” in your command prompt or shell), you can install it with the following command.
Linux Environment
$sudo apt-get install python-pip
Windows Environment
To install pip on Windows, follow these steps.
- Get pip from https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py href=”https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py”>or download get-pip.py from GitHub to your computer.
-
Open a command prompt and navigate to the folder containing the get-pip.py file.
-
Run the following command –
>python get-pip.py
That’s it, pip is now installed on your Windows machine.
You can verify that pip is installed by running the following command:
>pip --version
pip 19.2.3 from c:usersyadurappdatalocalprogramspythonpython37libsite-packagessip (Python 3.7)
Install a virtual environment
Run the following command in your command prompt:
>pip install virtualenv
After running, you should see the following screenshot:
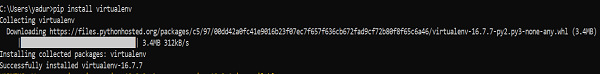
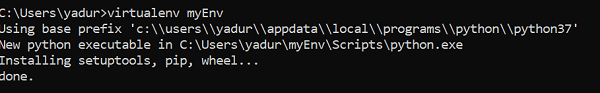
The following command will create a virtual environment (“myEnv”) in your current directory.
>virtualenv myEnv
Screenshot
To activate your virtual environment, run the following command –
>myEnvScriptsactivate
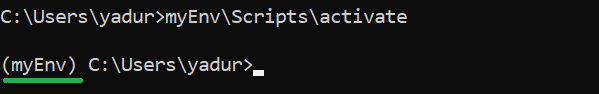
In the screenshot above, you can see that we have “myEnv” as the prefix, which tells us that we are in the virtual environment “myEnv.”
To exit the virtual environment, run deactivate.
(myEnv) C:Usersyadur>deactivate
C:Usersyadur>
Now that our virtual environment is ready, let’s install BeautifulSoup.
Installing BeautifulSoup
Since BeautifulSoup is not a standard library, we need to install it. We will use the BeautifulSoup 4 package (called bs4).
Linux Machines
To install bs4 using your system package manager on Debian or Ubuntu Linux, run the following commands:
$sudo apt-get install python-bs4 (for Python 2.x)
$sudo apt-get install python3-bs4 (for Python 3.x)
You can install bs4 using easy_install or pip (if you have problems installing using your system packager).
$easy_install beautifulsoup4
$pip install beautifulsoup4
(If you’re using Python 3, you may need to use easy_install3 or pip3, respectively.)
Windows Machines
Installing beautifulsoup4 on Windows is very simple, especially if you already have pip installed.
>pip install beautifulsoup4
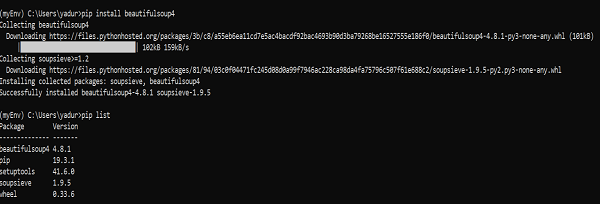
So now BeautifulSoup4 is installed on our machine. Let’s talk about some issues you might encounter after installation.
Post-Installation Issues
On Windows machines, you may encounter errors where the wrong version is installed, primarily through—
- Error: ImportError “No module named HTMLParser” , then you must run the Python 2 version of the code under Python 3.
-
Error: ImportError “No module named html.parser”, then you must run the Python 3 version of the code under Python 2.
The best way to get rid of both of these situations is to reinstall BeautifulSoup, completely removing the existing installation.
If you get a SyntaxError “Invalid syntax” on the line ROOT_TAG_NAME = u'[document]’, you need to convert your Python 2 code to Python 3. Simply install the package –
$ python3 setup.py install
Or manually run the Python 2 to 3 conversion script in the bs4 directory –
$ 2to3-3.2 -w bs4
Installing a parser
By default, Beautiful Soup supports the included in the Python standard library. rel=”noopener” target=”_blank” title=”HTML Tutorial”>HTML parser, however it also supports many external third-party python parsers, such as the lxml parser or the html5lib parser.
To install the lxml or html5lib parser, use the command —
Linux Machines
$apt-get install python-lxml
$apt-get install all python-html5lib
Windows Machines
$pip install lxml
$pip install html5lib
Generally speaking, users use lxml for speed. If you are using an older version of Python 2 (before 2.7.3) or Python 3 (and prior to 3.2.2), it’s recommended to use the lxml or html5lib parser, as Python’s built-in HTML parser doesn’t handle older versions very well.
Running Beautiful Soup
Now it’s time to test our Beautiful Soup package on an HTML page (using the webpage as an example – https://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm, but you can choose any other page you like) and extract some information from it.
In the following code, we attempt to extract the title from a webpage.
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm"
req = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(req.text, "html.parser")
print(soup.title)
Output
<title>H2O, Colab, Theano, Flutter, KNime, Mean.js, Weka, Solidity, Org.Json, AWS QuickSight, JSON.Simple, Jackson Annotations, Passay, Boon, MuleSoft, Nagios, Matplotlib, Java NIO,
<pre><code class="language-python line-numbers">for link in soup.find_all('a'):
print(link.get('href'))
Output
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/about/about_careers.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/questions/index.php
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/online_dev_tools.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/codingground.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/current_affairs.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/upsc_ias_exams.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/tutor_connect/index.php
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/whiteboard.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/netmeeting.php
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/tutorialslibrary.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/videotutorials/index.php
https://store.tutorialspoint.com
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/gate_exams_tutorials.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/html_online_training/index.asp p
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/css_online_training/index.asp
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/3d_animation_online_training/index.asp
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/swift_4_online_training/index.asp
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/blockchain_online_training/index.asp
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/reactjs_online_training/index.asp
https://www.tutorix.com
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/videotutorials/t op-courses.php
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/the_full_stack_web_development/index.asp
….
….
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/online_dev_tools.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/free_web_graphics.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/online_file_conversion.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/netmeeting.php
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/free_online_whiteboard.htm
http://www.tutorialspoint.com
https://www. facebook.com/tutorialspointindia
https://plus.google.com/u/0/+tutorialspoint
Tweets by tutorialspoint
http://www.linkedin.com/company/tutorialspoint
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVLbzhxVTiTLiVKeGV7WEBg
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm
/about/about_privacy.htm#cookies
/about/faq.htm
/about/about_helping.htm
/about/contact_us.htm
Similarly, we can use beautifulsoup4 to extract useful information.
Now let’s take a closer look at the “soup” in the above example.