Python XlsxWriter – Tables
Python XlsxWriter – Tables
In MS Excel, a table is a range of cells grouped as a single entity. It can be referenced from formulas and has common formatting properties. Features such as column headers, AutoFilters, row totals, and column formulas can be defined within a worksheet.
add_table() Method
The worksheet method add_table() is used to add a range of cells as a table.
worksheet.add_table(first_row, first_col, last_row, last_col, options)
Both methods allow the standard ‘A1‘ or ‘row/col‘ notation to specify the range. The add_table() method accepts one or more of the following optional parameters. Note that, except for the range parameter, all other parameters are optional. If not given, an empty table will be created.
Example
Data
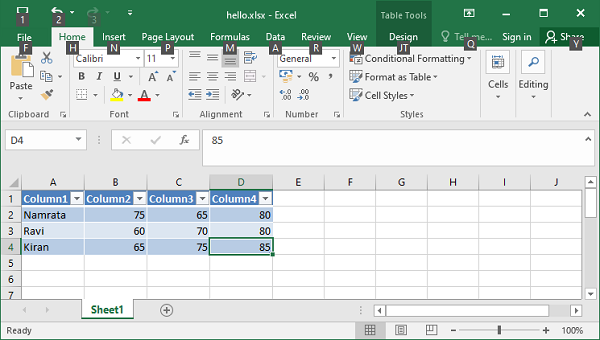
This parameter can be used to specify the data in the table’s cells. See the example below –
import xlsxwriter
wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
ws = wb.add_worksheet()
data = [
['Namrata', 75, 65, 80],
['Ravi', 60, 70, 80],
['Kiran', 65, 75, 85],
['Karishma', 55, 65, 75],
]
ws.add_table("A1:D4", {'data':data})
wb.close()
Output
Here is the result –
header_row
This parameter can be used to turn the header row in the table on or off. By default, it is on. The header row will contain default headings such as Column 1, Column 2, etc. You can set the desired headings using the columns parameter.
Columns
Example
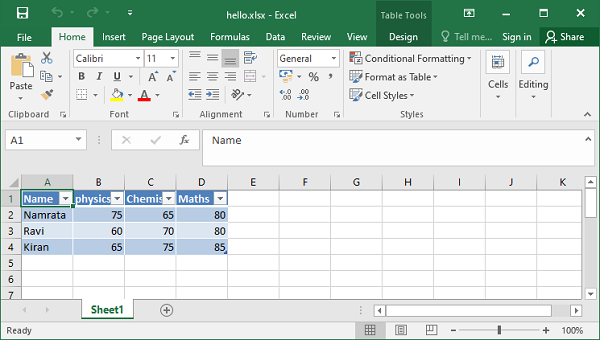
This property is used to set column headings.
import xlsxwriter
wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
ws = wb.add_worksheet()
data = [
['Namrata', 75, 65, 80],
['Ravi', 60, 70, 80],
['Kiran', 65, 75, 85],
['Karishma', 55, 65, 75],
]
ws.add_table("A1:D4",
{'data':data,
'columns': [
{'header': 'Name'},
{'header': 'physics'},
{'header': 'Chemistry'},
{'header': 'Maths'}]
})
wb.close()
Output
The header row is now set up as shown in the image –
AutoFilter
This parameter is on by default. When set to off, the header row does not display a drop-down arrow for setting filter conditions.
Name
In Excel worksheets, tables are named Table1, Table2, and so on. The Name parameter can be used to set the table name as desired.
ws.add_table("A1:E4", {'data':data, 'name':'marklist'})
Calculation Formulas
Columns with formulas can be created by specifying the formula subproperty in the column options.
Example
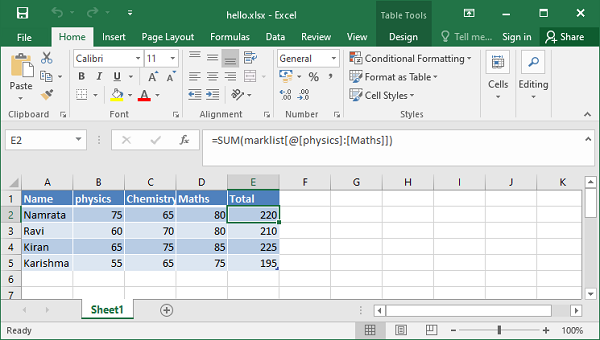
In the following example, the table’s name property is set to ‘marklist’. The formula in column E performs the sum of the scores and is assigned as the value of the formula sub-property.
import xlsxwriter
wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
ws = wb.add_worksheet()
data = [
['Namrata', 75, 65, 80],
['Ravi', 60, 70, 80],
['Kiran', 65, 75, 85],
['Karishma', 55, 65, 75],
]
formula = '=SUM(marklist[@[physics]:[Maths]])'
tbl = ws.add_table("A1:E5",
{'data': data,
'autofilter': False,
'name': 'marklist',
'columns': [
{'header': 'Name'},
{'header': 'physics'},
{'header': 'Chemistry'},
{'header': 'Maths'},
{'header': 'Total', 'formula': formula}
]
})
wb.close()
Output
When the above code is executed, the “Total” column in the worksheet displays the total of the scores.