RxPY – Overview
RxPY – Overview
This chapter explains what reactive programming is, what RxPY is, its operators, features, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is Reactive Programming
Reactive programming is a programming paradigm that deals with data streams and the propagation of changes. It means that when a component emits a stream of data, the change is propagated to other components through the reactive programming library. The propagation of the change continues until it reaches the final recipient.
By using RxPY, you can fine-tune asynchronous data flows. For example, you can track requests to a URL using observers and listen for responses or errors when the request completes.
RxPY provides you with the ability to process asynchronous data streams using Observables, query data streams using operators (e.g., filtering, summing, concatenating, and mapping), and execute concurrently using Schedulers. Create an Observable, given an observer object with on_next(v), on_error(e), and on_completed() methods. It needs to be subscribed to be notified when events occur.
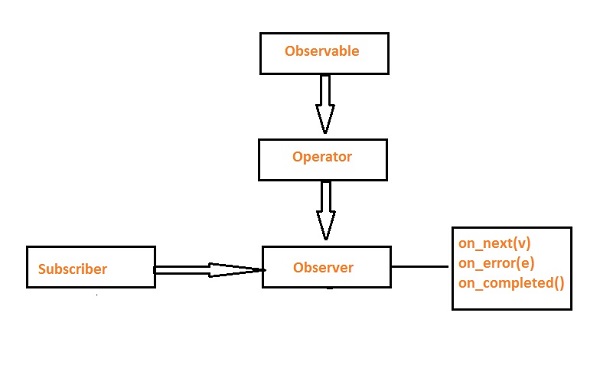
Using the pipe operator, an Observable can be queried using multiple operators in a chained fashion.
RxPY provides different categories of operators, such as: –
- Mathematical operators
-
Transformation operators
-
Filtering operators
-
Error handling operators
-
Utility operators
-
Conditional operators
-
Creation operators
-
Connectable operators
This tutorial explains these operators in detail.
What is RxPy?
According to the official RxPy website (https://rxpy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/), RxPY is defined as a library for composing asynchronous and event-based programs using observable collections and piped query operators in Python.
RxPY is a Python library that supports reactive programming. RxPy stands for Reactive Extensions for Python. It uses observers to handle reactive programming, handling asynchronous data calls, callbacks, and event-based programs.
RxPy Features
In RxPy, the following concepts handle asynchronous tasks:
Observables
An observer is a function that creates an observer and attaches it to a source with a stream of incoming data, such as tweets or computer-related events.
Observer
It is an object with on_next(), on_error(), and on_completed() methods, which are called when an interaction with the observer occurs, such as when the source interacts with incoming tweets.
Subscription
Once an observer is created, we need to subscribe to it in order to execute it.
Operators
An operator is a pure function that takes an observable as input and outputs an observable. You can use multiple operators on a single observable using the pipe operator.
Subject
A subject is an observable sequence and an observer that can multicast, meaning it can talk to many subscribed observers. A subject is a cold observer, meaning its values are shared among all subscribed observers.
Scheduler
A key feature of RxPy is concurrency, allowing tasks to execute in parallel. To achieve this, RxPy has two operators, subscribe_on() and observe_on() , which work together with a scheduler to determine when subscribed tasks should be executed.
Benefits of Using RxPY
Here are some of the advantages of using RxPy
-
RxPY is a great library for handling asynchronous data streams and events. RxPY uses observers to handle reactive programming for asynchronous data calls, callbacks, and event-based programs.
-
RxPY provides a wide range of operators in categories like math, transformations, filtering, utilities, conditionals, error handling, and joins, making life easier when using reactive programming.
-
Concurrency, where multiple tasks work together, is achieved through RxPY’s scheduler.
-
Using RxPY can improve performance because it makes it easy to handle asynchronous tasks and parallel processing.
Disadvantages of Using RxPY
- Debugging code with observables is a bit difficult.