Creating a weather forecast GUI in Python using the weatherstack API
Creating a Weather Forecast GUI in Python Using the Weatherstack API
What is the need for weather forecasts?
Weather forecasting is a crucial aspect of human existence. Recent technological advancements have made it easier to accurately predict the weather. OpenWeatherMap is a popular API that allows developers to retrieve weather data. In this tutorial, we will use the OpenWeatherMap API to create a graphical user interface (GUI) for weather forecasting in Python. This tutorial will cover the necessary steps required to build the GUI and retrieve data from the OpenWeatherMap API.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, we need to install a few things on your system
Recommended Setup List –
- Pip install tkinter
- It is expected that users will be accessing any standalone IDE, such as VS-Code, rel=”noopener” target=”_blank” title=”PyCharm Tutorial”>PyCharm, Atom, or Sublime Text.
- You can even use an online Python compiler, such as Kaggle.com, Google Cloud Platform, or any other platform.
- A newer version of Python. At the time of writing this article, I used version 3.10.9.
- Familiarity with using Jupyter notebooks.
- Knowledge and application of virtual environments is helpful, but not required.
- A good understanding of statistics and mathematics is also expected.
Steps Required to Complete the Task
Step 1: Import Necessary Modules
import tkinter as tk
import requests
The tkinter module is used to create GUI windows, labels, and input boxes. The requests module is used to make API requests to the WeatherStack API.
Step 2: Set up your Weatherstack API key
API_KEY = “your_weatherstack_api_key”
Replace your_weatherstack_api_key with your actual API key.
Step 3: Define the weather forecast URL
API_URL = “http://api.weatherstack.com/current”
This is the URL you will use to make requests to the Weatherstack API.
Step 4: Define the GUI window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Weather Forecast")
This will create the main GUI window and set its title to “Weather Forecast.”
Step 5: Define labels and input fields for cities and countries.
city_label = tk.Label(root, text="City:")
city_label.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=5, pady=5)
city_entry = tk.Entry(root)
city_entry.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
country_label = tk.Label(root, text="Country:")
country_label.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=5, pady=5)
country_entry = tk.Entry(root)
country_entry.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
This will create the label and input fields for the user to enter the city and country for which they want weather data.
Step 6: Define a function to get weather data from the API
def get_weather():
city = city_entry.get()
country = country_entry.get()
url = f"{API_URL}?access_key={API_KEY}&query={city},{country}"
# Send an API request and get a JSON response
response = requests.get(url).json()
# Get the relevant weather data from the JSON response
temperature = response["current"]["temperature"]
weather_desc = response["current"]["weather_descriptions"][0]
# In the GUI Display weather data in the GUI.
temperature_label.config(text=f"Temperature: {temperature}°C")
weather_desc_label.config(text=f"Weather description: {weather_desc}")
This function takes the city and country from the input fields, constructs the API request URL using the API key, city, and country, sends the request to the API, and extracts the relevant weather data from the JSON response. It then displays the temperature and weather description in the corresponding labels in the GUI.
Step 7: Define a button to get weather data
get_weather_button = tk.Button(root, text="Get Weather", command=get_weather)
get_weather_button.grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
This function creates a button that calls the get_weather function when clicked.
Step 8: Define labels for displaying weather data
temperature_label = tk.Label(root, text="")
temperature_label.grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
weather_desc_label = tk.Label(root, text="")
weather_desc_label.grid(row=4, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
These functions create the labels for displaying the temperature and weather description.
Step 9: Run the GUI window
root.mainloop()
This function starts the GUI and runs it until the user wants to close it.
Final Code and Program
import tkinter as tk
import requests
# Set your WeatherStack API key here
API_KEY = "your_weatherstack_api_key"
# Define the URL for the WeatherStack API
API_URL = "http://api.weatherstack.com/current"
# Define the GUI window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Weather Forecast")
# Define labels and input fields for city and country
city_label = tk.Label(root, text="City:")
city_label.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=5, pady=5)
city_entry = tk.Entry(root)
city_entry.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
country_label = tk.Label(root, text="Country:")
country_label.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=5, pady=5)
country_entry = tk.Entry(root)
country_entry.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
# Define a function to get weather data from the API
def get_weather():
city = city_entry.get()
country = country_entry.get()
# Construct a URL using the API key, city, and country
url = f"{API_URL}?access_key={API_KEY}&query={city},{country}"
# Send an API request and get a JSON response
response = requests.get(url).json()
# Get the relevant weather data from the JSON response
temperature = response["current"]["temperature"]
weather_desc = response["current"]["weather_descriptions"][0]
# Displaying weather data in the GUI
temperature_label.config(text=f"Temperature: {temperature}°C")
weather_desc_label.config(text=f"Weather description: {weather_desc}")
# Define a button for getting weather data
get_weather_button = tk.Button(root, text="Get Weather", command=get_weather)
get_weather_button.grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
# Define a label for displaying weather data
temperature_label = tk.Label(root, text="")
temperature_label.grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
weather_desc_label = tk.Label(root, text="")
weather_desc_label.grid(row=4, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
# Run GUI Window
root.mainloop()
# Define a button to get weather data
get_weather_button = tk.Button(root, text="Get Weather", command=get_weather)
get_weather_button.grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
# Define a label to display weather data
temperature_label = tk.Label(root, text="")
temperature_label.grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
weather_desc_label = tk.Label(root, text="")
weather_desc_label.grid(row=4, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=5, pady=5)
# Run the GUI Window
root.mainloop()
In this example, we first import the necessary libraries: tkinter and requests. We then set our Weatherstack API key and define the API URL. We use the tk.Tk() function to create a GUI window and set the window title.
We use the tk.Label() and tk.Entry() functions to create two labels and two input fields for the city and country. We then define a function called get_weather() to retrieve weather data from the API and display it in the GUI. This function uses the requests.get() function to send a GET request to the API URL with the city and country from the input fields. It then extracts the temperature and weather description data from the JSON response and updates the temperature and weather description labels in the GUI.
We use the tk.Button() function to create a button that retrieves weather data, setting the command parameter to the get_weather() function. We also create two labels to display the temperature and weather description data.
Finally, we use the root.mainloop() function to run the GUI window. When the user enters a city and country and clicks the “Get Weather” button, the get_weather() function will make a request to the API.
Output
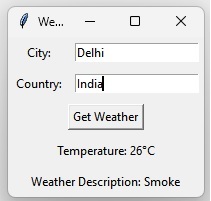
This image shows the output of the weather app GUI after we enter the city and country names. The API key will change based on the user’s needs.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to create a weather forecast GUI in Python using the Weatherstack API. We covered the steps necessary to build a GUI and retrieve data from the Weatherstack API. We also explained each subsection and provided a practical example of a weather forecast application using the Weatherstack API.