How to make text bold in CSS
How to Bold Text in CSS
Reference: how to bold text in CSS
Bolding text in CSS is a common task in web design and development. Bolding text increases its visual weight, making it stand out more and easier to read. With CSS, you can easily style text elements as bold without having to modify the HTML structure.
To bold text in CSS, use the font-weight property. This property accepts various numeric values or keywords, with bold being the most commonly used. Setting the font-weight to bold makes a text element appear bold.
Here is a simple HTML example showing how to make text bold using CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Bold Text Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS Style */
.bold-text {
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Bold Text Example -->
<p class="bold-text">This is bold text. </p>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:

In this example, we create a CSS class named bold-text and set its font-weight property to bold. Then, in the HTML, we apply this class to a paragraph element <p>, making the text within it appear bold.
This is a simple yet effective way to make text bold in CSS, providing more flexibility and control for web design and typography.
Technical Methods: Several Ways to Bold Text in CSS
Bolding text in CSS is a very basic yet very common skill. It can change the visual effect of text, making it more prominent and easier to read. In this section, we’ll delve into several methods for achieving bold text in CSS.
Method 1: Using the font-weight Property
The simplest and most direct way is to use the font-weight property. This property controls the weight of text. Its possible values are as follows:
normal: Normal font (default)bold: Bold fontbolder: Even bolder fontlighter: Even lighter font100to900: Numeric values indicating relative weight
Here is an example HTML and CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Text Bold Example</title>
<style>
/* Bold text */
.bold-text {
font-weight: bold; /* Use bold value */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is an example of <span class="bold-text">bold</span> text. </p>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:
Method 2: Use the <strong> tag
HTML provides the <strong> tag, which is designed to indicate important text. Browsers typically display it in bold. Use this tag if you want to maintain semantic clarity.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Bold Text Using the <strong> Tags</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is an example of <strong>bold</strong> text. </p>
</body>
</html>
The rendering of executing this code is:
Method 3: Using text-decoration and span >
While text-decoration is primarily used to control decorative effects (such as underlining) on text, it can also be combined with the span tag to achieve a bold effect.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Use text-decoration to make text bold</title>
<style>
/* Use text-decoration to make text bold */
.bold-text {
text-decoration: underline; /* Other decoration effects are also possible */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is an example of <span class="bold-text">bold</span> text. </p>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:
Method 4: Using a Custom Font
If you want more control over the weight of your text, you can use a custom font. By choosing a pre-designed font, you can achieve a more precise bolding effect. In this case, you need to use the @font-face rule to import the custom font and apply it in CSS.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Bold Text with Custom Font</title>
<style>
/* Import custom font */
@font-face {
font-family: 'CustomFont';
src: url('path/to/custom-font.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('path/to/custom-font.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: bold;
font-style: normal;
}
/* Apply custom font */
.bold-text {
font-family: 'CustomFont', sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is an example of bolding text with a <span class="bold-text">bold text</span>. </p>
</body>
</html>
The following image shows the effect of executing this code:
Summary
There are many ways to achieve bold text in CSS, each with its own application scenarios and advantages and disadvantages. Choose the method that works best for your project based on your project needs and personal preference. Whether using the simple font-weight property or combining it with HTML tags or custom fonts, you can easily achieve bold text. I hope this section helps you better understand and apply bold text techniques in CSS!
Common Problems and Solutions
Bolding text in CSS is a common requirement in web design. Whether it’s to highlight important information or enhance readability, bolding text is an effective method. However, developers may sometimes encounter common problems. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Question: How do I bold text with CSS?
Bolding text in CSS is very simple. You can achieve this using the font-weight property. This property controls the weight of the text and accepts the following values:
normal: Normal font (default)bold: Bold fontbolder: Even bolder fontlighter: Even lighter font<number>: A numeric value indicating the boldness relative to the parent elementinitial: Sets to the default valueinherit: Inherits the value from the parent element
Here is a simple example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Bold Text Example</title>
<style>
.bold-text {
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="bold-text">This is bold text. </p>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:

In this example, font-weight: bold; makes the text in the paragraph bold.
Solution: How to create a custom bold text effect?
Sometimes, developers may need a more customized bold effect to meet design requirements. This can be achieved by using other font properties, such as shadows and borders. Here’s an example of using text shadow to create a custom bold effect:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Custom Bold Text Effect</title>
<style>
.custom-bold-text {
text-shadow: 2px 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5); /* Set text shadow */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="custom-bold-text">This is a custom bold text effect. </p>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:

In this example, the text-shadow property creates a shadow effect on the text, making it appear bolder.
Question: How can I conditionally apply bold style?
Sometimes, developers may need to conditionally apply bold style, such as when the mouse is hovering or when an element is active. This can be achieved by using CSS pseudo-classes. Here’s an example that applies bold styling when the mouse hovers over text:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Bold Text on Hover</title>
<style>
.hover-bold-text:hover {
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="hover-bold-text">Hover your mouse here and the text will become bold. </p>
</body>
</html>
The following image shows the effect of executing this code:
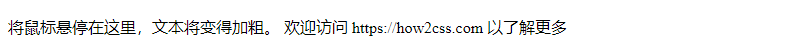
In this example, the .hover-bold-text:hover selector applies bold styles when the mouse hovers over the paragraph.
Solution: How to apply bold styles in responsive designs?
In responsive designs, developers may need to apply different bold styles based on different screen sizes or device types. This can be achieved using media queries. Here’s an example that applies bold text when the screen width is less than 600px:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Responsive Bold Text</title>
<style>
@media screen and (max-width: 600px) {
.responsive-bold-text {
font-weight: bold;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="responsive-bold-text">On smaller screens, this text will become bold. </p>
</body>
</html>
The following image shows the effect of executing this code:
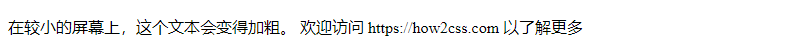
In this example, the .responsive-bold-text class will apply bold styling when the screen width is less than 600px.
By understanding these common problems and their solutions, developers can better understand how to make text bold in CSS and customize it to their needs.
Best practices for making text bold in CSS typically involve using the font-weight property. The font-weight property specifies the weight of text and can be set using keywords or numerical values.
Setting Weight Using Keywords
In CSS, we can use keywords to set text weight. Common keywords include normal, bold, bolder, and lighter. normal represents the standard font weight, bold represents a bold font, bolder represents a bolder font than the parent element, and lighter represents a lighter font than the parent element.
.bold-text {
font-weight: bold;
}
Setting Weight Using Numeric Values
In addition to keywords, we can also use numerical values to set font weight. The value ranges from 100 to 900, with higher values indicating bolder fonts. Generally, 400 is equivalent to normal, and 700 is equivalent to bold.
.heavy-text {
font-weight: 700;
}
Combining Uses
Sometimes, we need to use a combination of keywords and values to more precisely control the weight of text. For example, we can combine keywords and values to achieve a specific effect.
.custom-text {
font-weight: bold; /* Uses keywords to make the text bold */
font-weight: 600; /* Combined with a numeric value, makes the font slightly bolder */
}
Sample HTML Code
The following is a sample HTML code that demonstrates how to apply the above CSS styles:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Bold Text Example</title>
<style>
.bold-text {
font-weight: bold;
}
.heavy-text {
font-weight: 700;
}
.custom-text {
font-weight: bold; /* Use keyword to make text bold */
font-weight: 600; /* Combined with numerical value, makes the font slightly bolder */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="bold-text">This text is bold using keyword.</p>
<p class="heavy-text">This text is heavy using numerical value.</p>
<p class="custom-text">This text is custom bold using a combination of keyword and value.</p>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:

In the above code, we define three different text styles, using keywords, values, and a combination of keywords and values to set the font weight. This combination of methods provides developers with greater flexibility to meet different design needs.
Conclusion
Bolding text in CSS is a common requirement in web design. By using the font-weight property, we can easily achieve bold text. Furthermore, choosing the right font weight can help balance the visual effects of the page. In practice, bolding text not only improves readability but also helps emphasize important information, thereby improving the user experience.