Introduction to Python Web Scraping
Introduction to Web Scraping with Python
Web scraping is the automated process of retrieving information from the internet. This chapter will give you an in-depth understanding of web scraping, how it compares to web crawling, and why you should choose it. You’ll also learn about the components and workings of a web crawler.
What is Web Scraping
The dictionary definition of “scraping” is to obtain something from the internet. This raises two questions: What can we obtain from the internet, and how can we obtain it?
The answer to the first question is “data.” Data is indispensable for any programmer, and a basic requirement for every programming project is a large amount of useful data.
The answer to the second question is a bit tricky, as there are many ways to obtain data. Generally speaking, we can obtain data from databases, data files, and other sources. But what if we need a large amount of online data? One way to obtain this type of data is to manually search (click away in a web browser) and save (copy and paste into a spreadsheet or file) the required data. This method is quite tedious and time-consuming. Another way to obtain this type of data is to use a web scraper.
Web scraping, also known as web data mining or web harvesting, is the process of building an agent that automatically crawls, parses, downloads, and organizes useful information from the web. In other words, web scraping software automatically loads and crawls data from multiple websites based on your requirements, rather than manually saving website data.
Origins of Web Scraping
Web scraping has its origins in screen scraping, which was used to integrate non-web-based applications or native Windows applications. Initially, screen scraping was used before the widespread use of the World Wide Web (WWW), but it was unable to scale to the scale of the WWW. This necessitated the need to automate screen scraping methods, and thus the technique of web scraping was born.
Web Crawling vs. Web Scraping
The terms web crawling and scraping are often used interchangeably because their fundamental concept is to retrieve data. However, they are different. The basic difference can be understood from their definitions.
Web crawling is essentially using robots (also known as crawlers) to index information on web pages. It is also known as indexing. On the other hand, web scraping is an automated method of retrieving information using robots (also known as crawlers). It is also known as data scraping.
To understand the difference between the two terms, let’s take a look at the comparison table below.
| Web Crawling | Web Scraping |
|---|---|
| Refers to downloading and storing large amounts of website content. | Refers to the extraction of individual data elements from a website by exploiting the website’s specific structure. |
| Mostly performed on a large scale. | Can be implemented at any scale. |
| Generates general information. | Generates specific information. |
| Used by major search engines such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo. Googlebot is an example of a web crawler. | Information retrieved through web crawling can be replicated on other websites or used for data analysis. For example, data elements might be names, addresses, prices, etc. |
Uses of Web Scraping
The uses and reasons for using web scrapers are as endless as the uses of the World Wide Web. Web scrapers can do anything, like order food online, scan online shopping sites for you, buy tickets at a game, and so on, just like a human can. Some important uses of web scraping are discussed here.
- E-commerce Sites – Web scrapers can collect data related to the prices of specific products from various e-commerce sites for comparison purposes.
-
Content Aggregators – Web scrapers are widely used by content aggregators, such as news aggregators and job aggregators, to provide their users with the latest data.
-
Marketing and Sales Campaigns – Web scrapers can be used to obtain data such as email addresses, phone numbers, etc. for sales and marketing campaigns.
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) – Web scrapers are widely used by SEO tools like SEMRush and Majestic to tell businesses how they rank for relevant search terms.
-
Data for Machine Learning Projects – Data retrieval for machine learning projects depends on web scrapers.
Research Data – Researchers can save time and collect useful data for their research by automating this process.
Components of a Web Crawler
A web scraper consists of the following components
Web Crawler Module
A crucial component of a web scraper is the web scraper module, which is used to browse target websites by making HTTP or HTTPS requests to URLs. The scraper downloads unstructured data (HTML content) and passes it to the next module, the crawler.
Crawler
The crawler processes the retrieved HTML content and extracts the data into a semi-structured format. This is also known as a parser module and uses various parsing techniques, such as regular expressions, HTML parsing, DOM parsing, or artificial intelligence, to achieve its functionality.
Data Transformation and Cleansing Module
The crawled data above is not suitable for direct use. It must pass through some cleaning module before it can be used. Methods such as string processing or regular expressions can be used for this purpose. Note that crawling and transformation can also be performed in a single step.
Storage Module
After crawling the data, we need to store it according to our requirements. The storage module will output the data in a standardized format, which can be stored in a database, JSON, or CSV format.
Working of a Web Crawler
A web scraper can be defined as a software or script that downloads the content of multiple web pages and extracts data from them.
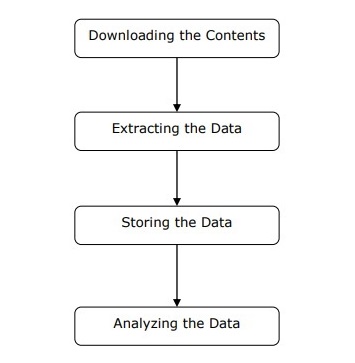
As shown in the figure above, we can understand the work of a web scraper in simple steps.
Step 1: Downloading Content from the Web Page
In this step, the web scraper will download the requested content from multiple web pages.
Step 2: Scrape the Data
The data on the website is HTML and is mostly unstructured. Therefore, in this step, the web scraper will parse and extract structured data from the downloaded content.
Step 3: Storing the Data
Here, the web scraper will store and save the scraped data in any format, such as CSV, JSON, or a database.
Step 4: Analyze the Data
After all these steps are successfully completed, the web scraper will analyze the resulting data.