Matplotlib Tutorial
Matplotlib Tutorial shows how to use Matplotlib in Python creates charts. We create scatter plots, line charts, bar charts, and pie charts.
Matplotlib
Matplotlib is the Python library for creating charts. Matplotlib can be used in Python scripts, the Python and IPython shells, Jupyter notebooks, web application servers, and four graphical user interface toolkits.
Matplotlib Installation
Matplotlib is an external Python library that needs to be installed.
$ sudo pip install matplotlib
We can install this library using the pip tool.
Matplotlib Scatter Plot
A scatter plot is a graph or mathematical plot that displays the values of two variables in a set of data using Cartesian coordinates.
scatter.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
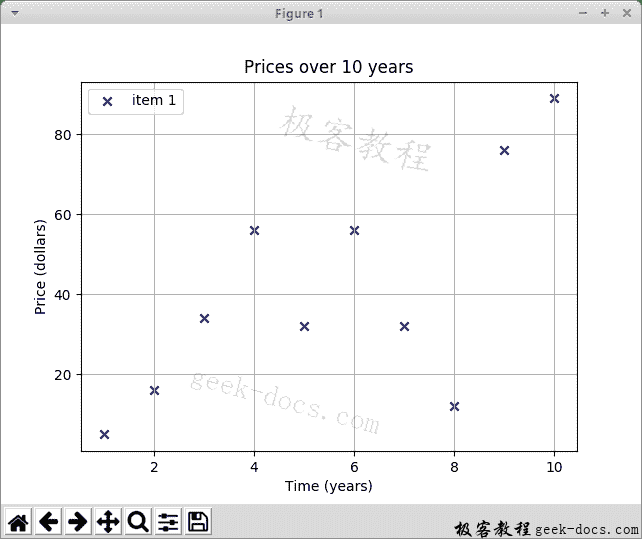
x_axis = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y_axis = [5, 16, 34, 56, 32, 56, 32, 12, 76, 89]
plt.title("Prices over 10 years")
plt.scatter(x_axis, y_axis, color='darkblue', marker='x', label="item 1")
plt.xlabel("Time (years)")
plt.ylabel("Price (dollars)")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
This example creates a scatter plot. The chart shows the prices of certain commodities over a ten-year period.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
We import pyplot from the matplotlib module. It is a collection of command-style functions for creating charts. Its operations are similar to those of MATLAB.
x_axis = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y_axis = [5, 16, 34, 56, 32, 56, 32, 12, 76, 89]
We have data for the x- and y-axes.
plt.title("Prices over 10 years")
Using the title() function, we can set a title for the chart.
plt.scatter(x_axis, y_axis, color='darkblue', marker='x', label="item 1")
The
scatter() function draws a scatter plot. It accepts the x and y axes, the marker color, the marker shape, and the label data.
plt.xlabel("Time (years)")
plt.ylabel("Price (dollars)")
We set the axis labels.
plt.grid(True)
We use the grid() function to display a grid. A grid consists of a number of vertical and horizontal lines.
plt.legend()
The
legend() function places a legend on the axes.
plt.show()
The
show() function displays the chart.
Two Datasets
In the next example, we add another dataset to the chart.
scatter2.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_axis1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y_axis1 = [5, 16, 34, 56, 32, 56, 32, 12, 76, 89]
x_axis2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y_axis2 = [53, 6, 46, 36, 15, 64, 73, 25, 82, 9]
plt.title("Prices over 10 years")
plt.scatter(x_axis1, y_axis1, color='darkblue', marker='x', label="item 1")
plt.scatter(x_axis2, y_axis2, color='darkred', marker='x', label="item 2")
plt.xlabel("Time (years)")
plt.ylabel("Price (dollars)")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
This chart shows two data sets. We distinguish them by the color of the markers.
x_axis1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y_axis1 = [5, 16, 34, 56, 32, 56, 32, 12, 76, 89]
x_axis2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y_axis2 = [53, 6, 46, 36, 15, 64, 73, 25, 82, 9]
We have two datasets.
plt.scatter(x_axis1, y_axis1, color='darkblue', marker='x', label="item 1")
plt.scatter(x_axis2, y_axis2, color='darkred', marker='x', label="item 2")
We call the scatter() function for each set.
Matplotlib Line Chart
A line chart is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points connected by straight line segments, called markers.
linechart.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
t = np.arange(0.0, 3.0, 0.01)
s = np.sin(2.5 * np.pi * t)
plt.plot(t, s)
plt.xlabel('time (s)')
plt.ylabel('voltage (mV)')
plt.title('Sine Wave')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
This example displays a sine wave line chart.
import numpy as np
In this example, we also need the numpy module.
t = np.arange(0.0, 3.0, 0.01)
The
arange() function returns a list of evenly spaced values within a given interval.
s = np.sin(2.5 * np.pi * t)
We obtain the sin() values of the data.
plt.plot(t, s)
We use the plot() function to draw a line chart.
Matplotlib Bar Charts
A bar chart displays grouped data with rectangular bars whose lengths are proportional to the values they represent. Bars can be drawn vertically or horizontally.
barchart.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import style
style.use('ggplot')
x = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y = [46, 38, 29, 22, 13, 11]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.bar(x, y, align='center')
ax.set_title('Olympic Gold medals in London')
ax.set_ylabel('Gold medals')
ax.set_xlabel('Countries')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(("USA", "China", "UK", "Russia", "South Korea", "Germany"))
plt.show()
This example plots a bar chart. It shows the number of Olympic gold medals for each country in London 2012.
style.use('ggplot')
You can use predefined styles.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
The
subplots() function returns a figure and axes object.
ax.bar(x, y, align='center')
Use the bar() function to generate a bar chart.
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(("USA", "China", "UK", "Russia",
"South Korea", "Germany"))
We set the country names for the x-axis.
Matplotlib Pie Chart
A pie chart is a circular graph that is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions.
piechart.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
labels = ['Oranges', 'Pears', 'Plums', 'Blueberries']
quantity = [38, 45, 24, 10]
colors = ['yellowgreen', 'gold', 'lightskyblue', 'lightcoral']
plt.pie(quantity, labels=labels, colors=colors, autopct='%1.1f%%',
shadow=True, startangle=90)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.show()
This example creates a pie chart.
labels = ['Oranges', 'Pears', 'Plums', 'Blueberries']
We have labels and corresponding quantities.
colors = ['yellowgreen', 'gold', 'lightskyblue', 'lightcoral']
We define the colors for the pie slices.
plt.pie(quantity, labels=labels, colors=colors, autopct='%1.1f%%',
shadow=True, startangle=90)
The pie chart is generated using the pie() function. autopct is responsible for displaying percentages in the wedges of the chart.
plt.axis('equal')
We set an equal aspect ratio so that the pie charts are drawn as circles.
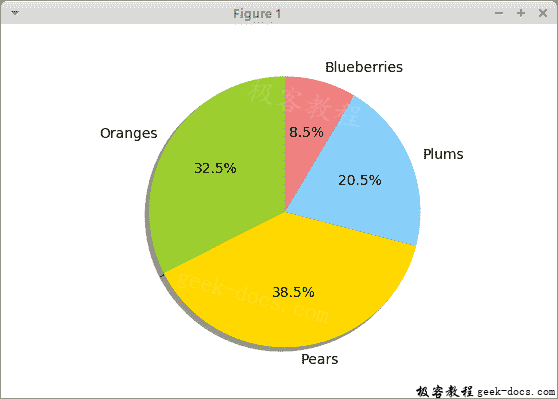
Figure: Pie chart
In this tutorial, we created a scatter plot, a line chart, a bar chart, and a pie chart using the Matplotlib library.
You may also be interested in the following related tutorials: PrettyTable Tutorial, SymPy Tutorial, Python Tutorial.