Python Forensics – Basic Forensics Applications
Python Forensics – Basic Forensic Applications
To create an application that complies with forensic guidelines, it is important to understand and follow naming conventions and patterns.
Naming Rules
The following table describes the rules and conventions that should be followed when developing Python forensic applications.
| Constants | Uppercase letters, separated by underscores | high_temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Local variable names | Lowercase, with raised capitals (underscores are optional) | currentTemperature |
| Global variable names | The prefix gl is lowercase, with raised capitals (underscores are optional). | gl_maximumRecordedTemperature (maximum recorded temperature). |
| Function Name | Uppercase, raised capitals (underscores are optional), with active voice | ConvertFarenheitToCentigrade(…) |
| Object Name | Prefix ob_ in lowercase, raised capitals | ob_myTempRecorder |
| Module | An underscore followed by lowercase raised capitals | _tempRecorder |
| Class Name | Start with class_, followed by raised capitals, and keep it short. | class_TempSystem |
Let’s use a scenario to understand the importance of naming conventions in computational forensics. Suppose we have a hashing algorithm commonly used to encrypt data. A one-way hashing algorithm takes as input a stream of binary data; this could be a password, a file, binary data, or any digital data. The hashing algorithm then produces a message digest (MD) associated with the input data.
It is virtually impossible to create a new binary input that produces a given message digest. Changing even a single bit of the binary input data will produce a unique message that is different from the previous message.
Example
Please see the following example program that follows the above conventions.
import sys, string, md5 # necessary libraries
print "Please enter your full name"
line = sys.stdin.readline()
line = line.rstrip()
md5_object = md5.new()
md5_object.update(line)
print md5_object.hexdigest() # Prints the output as per the hashing algorithm, i.e., md5
exit
The above program produces the following output.
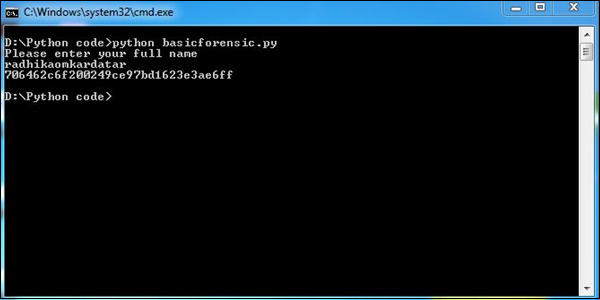
In this program, the Python script accepts input (your full name) and converts it according to the MD5 hashing algorithm. If necessary, it encrypts the data and protects the information. According to forensic guidelines, the name of the evidence or any other proof can be secured using this pattern.