Python Forensics – Hash Functions
Python Forensics – Hash Functions
A hash function is defined as a function that maps a large amount of data to a fixed value of a specified length. This function ensures that the same input produces the same output, which is essentially defined as the hash sum. The hash sum includes a characteristic that has specific information.
This function is virtually impossible to reverse. Therefore, any third-party attack, such as a brute force attack, is effectively impossible. Furthermore, this algorithm is known as a one-way encryption algorithm.
An ideal cryptographic hash function has four main properties
- For any given input, it must be easy to calculate a hash value.
- It must be infeasible to generate the original input from its hash value.
- It must be infeasible to modify the input without changing the hash value.
- It must be infeasible to find two different inputs that have the same hash value.
Example
See the following example, which helps match passwords using hexadecimal characters.
import uuid
import hashlib
def hash_password(password):
# userid is used to generate a random number
salt = uuid.uuid4().hex #salt is stored in hexadecimal value
return hashlib.sha256(salt.encode() + password.encode()).hexdigest() + ':' + salt
def check_password(hashed_password, user_password):
# hexdigest is used as an algorithm for storing passwords
password, salt = hashed_password.split(':')
return password == hashlib.sha256(salt.encode()
+ user_password.encode()).hexdigest()
new_pass = raw_input('Please enter required password ')
hashed_password = hash_password(new_pass)
print('The string to store in the db is: ' + hashed_password)
old_pass = raw_input('Re-enter new password ')
if check_password(hashed_password, old_pass):
print('Yuppie!! You entered the correct password')
else:
print('Oops! I am sorry but the password does not match')
Flowchart
We have explained the logic of this program with the help of the following flowchart —
Output
Our code will produce the following output –
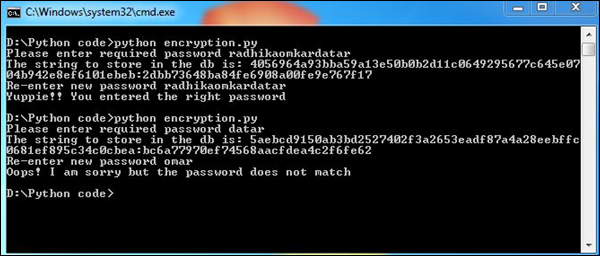
The password entered twice is matched with the hash function. This ensures that the passwords entered twice are accurate, which helps collect useful data and save it in encrypted form.