Python Forensics – Network Forensics
Python Forensics – Network Forensics
Modern network environments are such that investigations can be fraught with difficulties. This can occur when you are responding to vulnerability support requests, investigating internal activities, performing vulnerability-related assessments, or verifying regulatory compliance.
Network Programming Concepts
The following are definitions used in network programming.
- Client – The client is part of the client-server architecture of network programming and runs on personal computers and workstations.
-
Server – The server is part of the client-server architecture and provides services to other computer programs on the same or other computers.
-
WebSockets – WebSockets provides a protocol between a client and a server that runs over a persistent TCP connection. It allows bidirectional (simultaneous) information to be sent between the TCP sockets.
WebSockets emerged from a number of other technologies that allow servers to send information to clients. Aside from the handshake upgrade header, WebSockets is independent of HTTP.
These protocols are used to authenticate information sent or received by third-party users. Since encryption is one of the methods used to ensure information security, ensuring the security of the transmission channel is also important.
Consider the following Python program, which the client uses to perform a handshake.
Example
# client.py
import socket
# create a socket object
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# get local machine name
host = socket.gethostname()
port = 8080
# connect to hostname on the port.
s.connect((host, port))
# receive no more than 1024 bytes
tm = s.recv(1024)
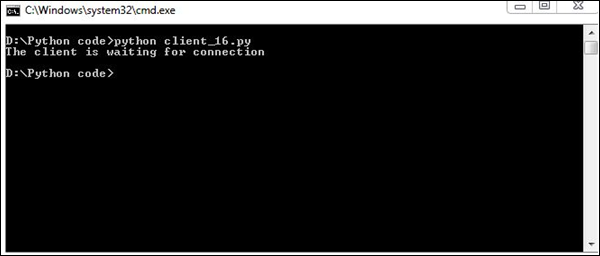
print("The client is waiting for connection")
s.close()
Output
It will produce the following output –
The server accepting communication channel requests will include the following script.
# server.py
import socket
import time
# create a socket object
serversocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# get local machine name
host = socket.gethostname()
port=8080
# bind to the port
serversocket.bind((host, port))
# queue up to 5 requests
serversocket.listen(5)
while True:
#establish a connection
clientsocket,addr = serversocket.accept()
print("Got a connection from %s" % str(addr))
currentTime = time.ctime(time.time()) + "rn"
clientsocket.send(currentTime.encode('ascii')) clientsocket.close()
Using Python programming, we create a client and server that listens to a host number. Initially, the client sends a request to the server, specifying the data sent in the host number. The server accepts the request and immediately responds. This creates a secure communication channel.