Python Pillow – Working with Images
Python Pillow – Working with Images
In this article, we’ll see how to use Pillow to work with images in Python. We’ll discuss basic operations like creating, saving, and rotating images. So let’s get started, but first, let’s see how to install Pillow.
Installation
To install the package, type the following command in your terminal.
pip install pillow
Creating a New Image
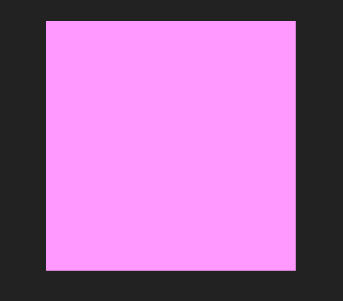
You can create a new image using the PIL.Image.new() method. This method creates a new image with the given mode and dimensions. The dimensions are a 4-tuple (width, height) in pixels.
Syntax: PIL.Image.new(mode, size, color)
Code:
import PIL
image = PIL.Image.new(mode = "RGB",
size = (200, 200),
color = (255, 153, 255))
image.show()
Output:
Opening Images
You can open any image using the PIL.Image.open() method.
Syntax: PIL.Image.open(fp, mode='r')
Code:
from PIL import Image
image = Image.open('nature.jpg')
image.show()
Output:

Getting Information About an Image
- Getting the Image Format: The obj.format method returns the format of an image file.
from PIL import Image
img = Image.open("test.png")
print(img.format)
Output:
PNG
- Getting the image size: The obj.size attribute provides the image size. It returns a tuple containing the width and height.
from PIL import Image
img = Image.open("test.png")
print(img.size)
Output:
(180, 263)
Renaming and Saving Images
We can change the image’s name and format, and even rename it using the image.save() method.
Syntax: Image.save(fp, format=None, **params)
Code:
from PIL import Image
image = Image.open('nature.jpg')
image.show()
image.save('nature1.bmp')
image1 = Image.open('nature1.bmp')
image1.show()
Output:
Before
After change
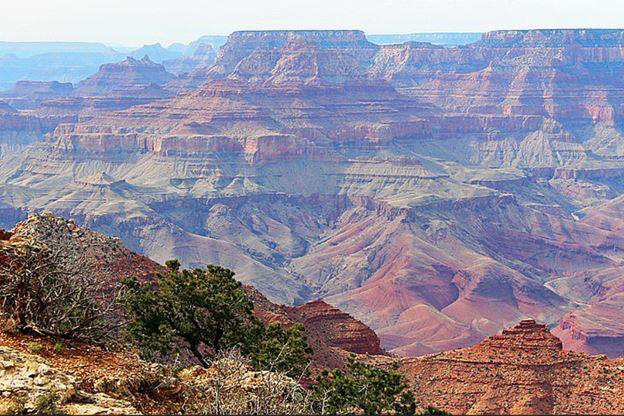
Cropping an Image
PIL is the Python Imaging Library, which provides image editing capabilities for the Python interpreter. The PIL.Image.crop() method is used to crop a rectangular portion of any image.
Syntax: PIL.Image.crop(box = None)
Code:
from PIL import Image
# Open image
im = Image.open("nature.jpg")
# Show actual image
im.show()
# Show cropped image
im = im.crop((0,0,50,50)
im.show()
Output:

Before rotation
Cropped Image
Rotating an Image
The PIL.Image.Image.rotate() method rotates the given image a specified number of degrees counterclockwise around its center.
Syntax: new_object = PIL.Image.Image.rotate(image_object, angle, resample=0, expand=0) OR new_object = image_object.rotate(angle, resample=0, expand=0)
Code:
from PIL import Image
# Open image
im = Image.open("nature.jpg")
# Show actual Image
im.show()
# Show rotated Image
im = im.rotate(45)
im.show()
Output:
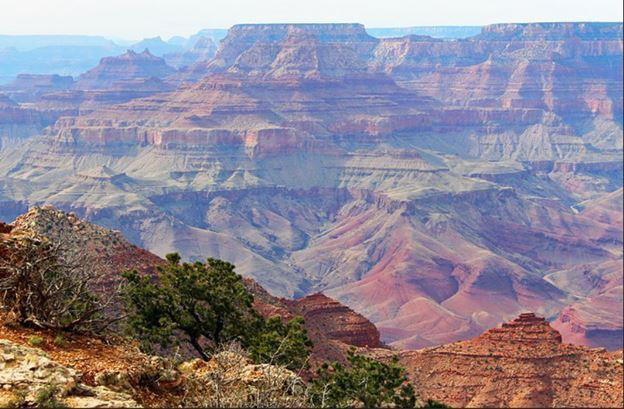

Before rotation

After Rotation
Filtering Images
The current version of the Pillow library provides the following set of predefined image enhancement filters.
- BLUR
- CONTOUR
- DETAIL
- EDGE_ENHANCE
- EDGE_ENHANCE_MORE
- EMBOSS
- FIND_EDGES
- SHARPEN
- SMOOTH
- SMOOTH_MORE
The ImageFilter module contains definitions for a set of predefined filters that can be used with the Image.filter() method.
Syntax: Filter(Kernel)
Takes a kernel (predefined or custom) and passes it through each pixel of the image (kernel convolution).
Code:
# Import required image modules
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter
# Import all the enhancement filters from pillow
from PIL.ImageFilter import (
BLUR, CONTOUR, DETAIL, EDGE_ENHANCE, EDGE_ENHANCE_MORE,
EMBOSS, FIND_EDGES, SMOOTH, SMOOTH_MORE, SHARPEN
)
# Create image object
img = Image.open('nature.jpg')
# Applying the sharpen filter
# You can change the value in the filter function
# to see the deifferences
img1 = img.filter(SHARPEN)
img1.show()
Output:
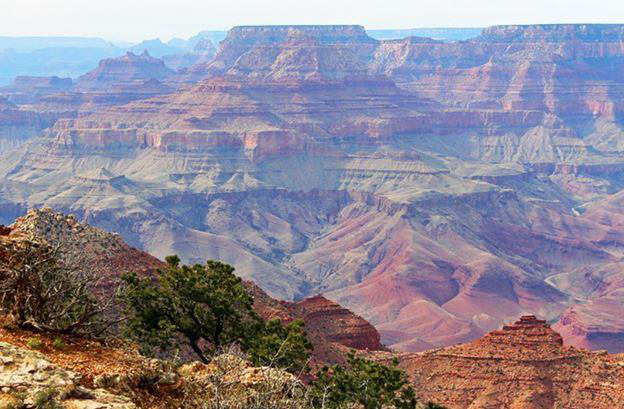

Before filter

After Sharpen Filtering
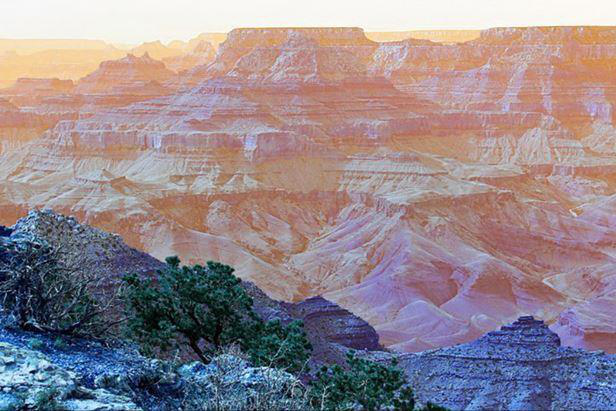
Creating a Watermark on an Image
Here, you create a watermark by using ImageDraw.Draw.text(), which draws a string at a given location.
Syntax: ImageDraw.Draw.text(xy, text, fill=None, font=None, anchor=None, spacing=0, align=”left”)
Code:
# Import required Image libraries
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
# Create an Image Object from an Image
im = Image.open('nature.jpg')
width, height = im.size
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im)
text = "lovely nature"
font = ImageFont.truetype('arial.ttf', 36)
textwidth, textheight = draw.textsize(text, font)
# Calculate the x,y coordinates of
# the text
x = 100
y = 50
# Draw a watermark in the bottom right corner
# corner
draw.text((x, y), text, font=font)
im.show()
# Save the watermarked image
im.save('watermark.jpg')
Output:

Before Watermark/text

After Watermark/text
