Python program to add elements to a linked list
Python Program to Add Elements to a Linked List
What is a Linked List
When data is not stored in consecutive memory locations, searching all memory locations to retrieve the desired data takes a considerable amount of time. To prevent this, we use linked lists.
In Python, a linked list is a data structure that stores items sequentially. It consists of nodes, each of which contains an item and a reference to the next node in the list. The first node is called the head, and the last node is called the tail.
Linked lists allow for efficient insertion and deletion operations because new items can be added or removed at any position in the list without having to move all the surrounding elements. Additionally, they take up less memory space than arrays because only references need to be stored, rather than copies of each element.
Linked lists are composed of nodes. Each node contains
- Data
-
A link to the next node (usually a pointer)
HEAD will contain a link to the first node. The last node will point to NULL. There are three ways to add an element to a linked list: you can add it to the beginning, the end, or the middle (anywhere except the beginning and the end).
Adding Elements at the Beginning
A new node is added to the head of the linked list. The newly added node becomes the head of the linked list.
Consider a linked list with three nodes: A, B, and C. You want to add a new node, D, to the beginning.
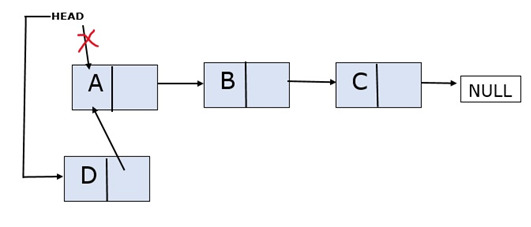
Algorithm
Step 1 – First, create a new node to be added to the beginning of the linked list and assign data to it.
Step 2 – Now, point the new node to the head.
Step 3 – Make the head point to the address of the newly created node.
Function Implementation
def insert_at_the_beginning(self, newVal):
newNode = Node(newVal) # Creating the new node
newNode.next = self.head # Point the new node to the previous first node
self.head = newNode # Point the head to the newly added node
Adding an Element to the End
Adds a new node after the last node. The new node points to NULL. Consider a linked list with three nodes: A, B, and C. You want to add a new node, D, to the end.
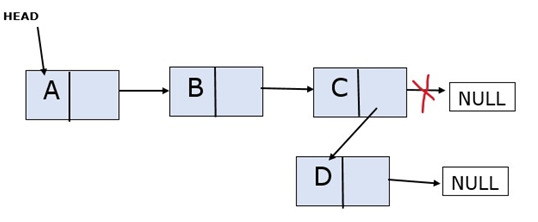
Algorithm
Step 1 – Create a new node to be added to the beginning of the linked list, assign data, and set it to point to NULL.
Step 2 – Traverse to the end of the linked list (when you encounter NULL, the linked list ends)
Step 3 – Make the last node point to the newly created node
Function Implementation
def insert_at_the_end(self, newVal):
newNode=Node(newVal)
temp=self.head
while(temp.next):
temp=temp.next
temp.next=newNode
Adding an Element in the Middle
The position where the new node is to be inserted is given along with the data. We need to insert the new node at that position.
Consider a linked list with four nodes: A, B, C, and D. A new node E must be inserted at position 3 (after node B).
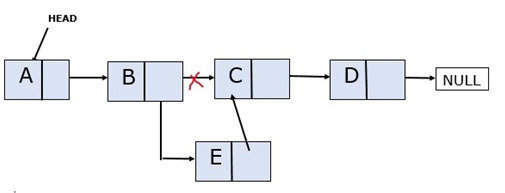
Algorithm
Step 1 – Create a new node to be added to the middle of the linked list and assign data.
Step 2 – Traverse the list until it reaches the position before the new node.
Step 3 – Assume you want to insert a new node at position “x”.
-
Traverse until x-1.
-
Point the new node to (x-1.next).
-
Set x-1 to point to the new node.
Function implementation
def insert_in_middle(self,newVal,pos):
newNode=Node(newVal)
temp=self.head
for i in range(2,pos):
if temp.next!=None:
temp=temp.next
newNode.next=temp.next
temp.next=newNode
Python code
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_the_beginning(self, newVal):
newNode = Node(newVal) #Create a new node
newNode.next = self.head # Connect the new node to the previous first node
self.head = newNode # Set the head pointer to the newly added node
def insert_at_the_end(self, newVal):
newNode = Node(newVal)
temp = self.head
while(temp.next):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = newNode
def insert_in_middle(self, newVal, pos):
newNode = Node(newVal)
temp = self.head
for i in range(2, pos): # Used to iterate over the positions to insert the new node
if temp.next != None:
temp = temp.next
newNode.next = temp.next
temp.next = newNode
def print_the_LL(self):
temp = self.head
if(temp != None):
print("The linked list elements are:", end = "")
while(temp != None):
print(temp.val, end = "")
temp = temp.next
else:
print("The list is empty.")
newList = LinkedList()
print("Please enter the number of elements to add to the linked list: ")
n=int(input())
for i in range(n):
print("Choose from: 1. Beginning 2. End 3. Middle")
a=int(input())
if(a == 1):
print("Enter data: ")
data=int(input())
newList.insert_at_the_beginning(data)
elif(a == 2):
print("Enter data: ")
data=int(input())
newList.insert_at_the_end(data)
else:
print("Enter position: ")
pos=int(input())
print("Enter data: ")
data=int(input())
newList.insert_in_middle(data, pos)
newList.Print_the_LL()
Output
Please enter the number of elements to add to the linked list:
3
Choose from: 1. Beginning 2. End 3. Middle
1
Input data:
112
Choose from: 1. Beginning 2. End 3. Middle
2
Input data:
145
Choose from: 1. Beginning 2. End 3. Middle
3
Input position:
2
Input data:
223
The linked list elements are: 112 223 145