Python program to detect cycles in linked lists
Python Program to Detect Cycles in a Linked List
A linked list is said to have a cycle when no node in it points to NULL. The last node will point to a previous node in the linked list, creating a cycle. A linked list with a cycle will not end.
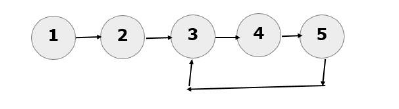
In the example below, the last node (node 5) does not point to NULL. Instead, it points to node 3, creating a cycle. Therefore, the linked list above has no end.
Algorithm – Using Two Pointers: Fast and Slow
- Both pointers initially point to the head of the linked list.
-
The slow pointer will always increase by 1, and the fast pointer will always increase by 2.
-
At any point, if both the fast and slow pointers point to the same node, then there is a cycle in the linked list.
Consider the following linked list example, where the last node points to the second node −
Example
Both the slow pointer and the fast pointer point to the same node. Therefore, we can conclude that the given linked list contains a cycle.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_the_end(self,newVal):
newNode=Node(newVal)
if self.head==None:
self.head=newNode
return
temp=self.head
while(temp.next):
temp=temp.next
temp.next=newNode
def Print_the_LL(self):
temp = self.head
if(temp != None):
print("nThe linked list elements are:", end=" ")
while (temp != None):
print(temp.val, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
else:
print("The list is empty.")
def detect_loop(self):
slow=self.head fast=self.head
while(fast):
if slow==fast:
print("nA loop has been detected in the linked list ")
return
slow=slow.next
fast=fast.next
newList = LinkedList()
newList.insert_at_the_end(1)
newList.insert_at_the_end(2)
newList.insert_at_the_end(3)
newList.insert_at_the_end(4)
newList.Print_the_LL()
print("n")
newList.head.next.next.next.next=newList.head.next
newList.detect_loop()
Output
A cycle was detected in the linked list.
The linked list elements are: 1 2 3 4
A loop has been detected in the linked list