Python program to implement binary tree data structure
Python Program to Implement the Binary Tree Data Structure
A tree is a data structure composed of nodes. Nodes are connected by edges. The topmost node is called the root, and the bottommost nodes are called leaf nodes. Leaf nodes are nodes that have no children.
Binary Tree
A binary tree is a tree in which each node can have at most two children. In other words, each node can have zero, one, or two children, but never more than two. Each node in a binary tree contains three fields:
- Data
-
Pointer to the left child
-
Pointer to the right child
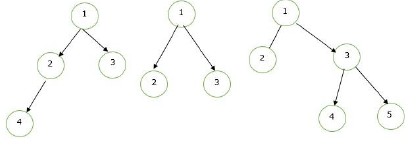
Complete Binary Tree – A complete binary tree is one where all levels are completely filled, except for the last, and all nodes are kept as far to the left as possible.
Strict/Formal Binary Tree – A strict or formal binary tree is one where each node has either zero or two children.
Perfect Binary Tree – A binary tree is called perfect if all nodes have two children and all leaf nodes are at the same level.
Balanced Binary Tree – A binary tree is called balanced if the difference between the height of the left subtree and the height of the right subtree is at most 1 (either 0 or 1).
Build a Binary Tree from a Given Array
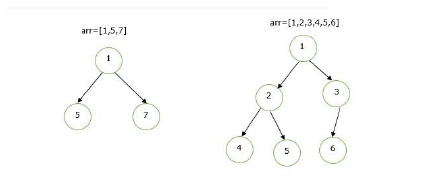
Example
If the root node is at index i, the left child will be at (2 * i + 1) and the right child will be at (2 * i – 1). We will use this concept to build a binary tree from array elements.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self,data,left=None,right=None):
self.data=data
self.left=left
self.right=right
def insert_into_tree(root,arr,i,l):
if i<l:
print(arr[i])
temp=TreeNode(arr[i])
root=temp
root.left=insert_into_tree(root,arr,i*2+1,l)
root.right=insert_into_tree(root,arr,i*2+2,l)
return root
arr=[1,2,3,4,5]
i=0
l=len(arr)
root=TreeNode(arr[0])
insert_into_tree(root,arr,i,l)
Output
1
2
4
5
3