Python random.paretovariate()
Python random.paretovariate()
The random module is used to generate random numbers in Python. These numbers are not actually random, but rather pseudo-random. This means that the numbers generated are deterministic.
random.paretovariate()
paretovariate() is a built-in method of the random module. It returns a random floating-point number with a Pareto distribution.
Syntax: random.paretovariate(alpha).
Parameters:
alpha: Shape parameter
Returns: A random Pareto-distributed floating-point number
Example 1:
# import the random module
import random
# determining the values of the parameter
alpha = 3
# using the paretovariate() method
print(random.paretovariate(alpha))
Output:
1.0333528834896462
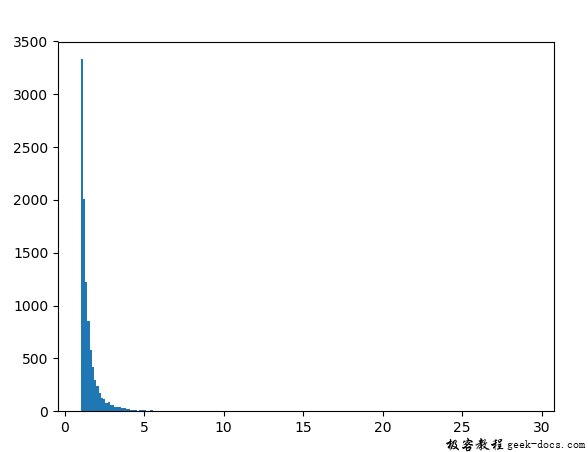
Example 2: We can generate numbers multiple times and plot a graph to observe the Pareto distribution.
# import the required libraries
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# store the random numbers in a
# list
nums = []
alpha=3
for i in range(100):
Temp = random.paretovariate(alpha)
nums.append(temp)
# plotting a graph
plt.plot(nums)
plt.show()
Output:
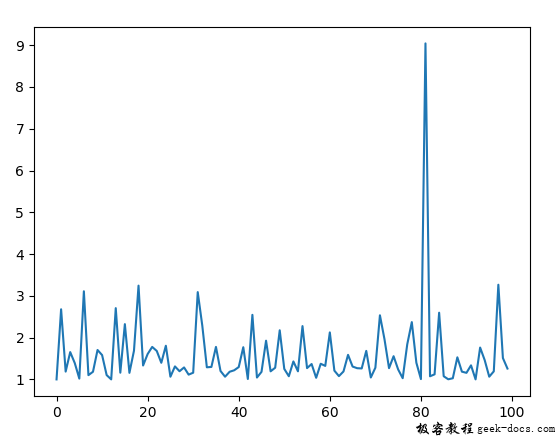
Example 3: We can create a histogram to visualize the density of the Pareto distribution.
# import the required libraries
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# store the random numbers in a list
nums = []
alpha=3
for i in range(10000):
Temp = random.paretovariate(alpha)
nums.append(temp)
# plotting a graph
plt.hist(nums, bins = 200)
plt.show()
Output: