Python XlsxWriter – Fonts and Colors
Python XlsxWriter – Fonts and Colors
Working with Fonts
To perform worksheet cell formatting, we need to use the Format object with the help of the add_format() method and configure it through its properties or formatting methods.
f1 = workbook.add_format()
f1 = set_bold(True)
# or
f2 = wb.add_format({'bold':True})
This format object is then used as a parameter to the worksheet’s write() method.
ws.write('B1', 'Hello World', f1)
Example
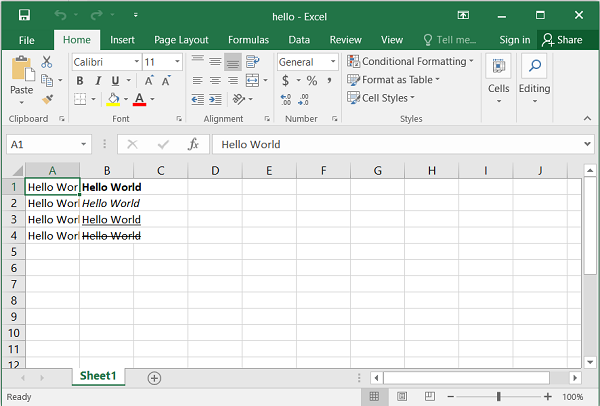
To make text in a cell bold, underlined, italic, or struck through, we can use these properties or corresponding methods. In the example below, the text “Hello World” is written using the setter methods.
import xlsxwriter
wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
ws = wb.add_worksheet()
for row in range(4):
ws.write(row,0, "Hello World")
f1=wb.add_format()
f2=wb.add_format()
f3=wb.add_format()
f4=wb.add_format()
f1.set_bold(True)
ws.write('B1', '=A1', f1)
f2.set_italic(True)
ws.write('B2', '=A2', f2)
f3.set_underline(True)
ws.write('B3', '=A3', f3)
f4.set_font_strikeout(True)
ws.write('B4', '=A4', f4)
wb.close()
Output
Here is the result –
Example
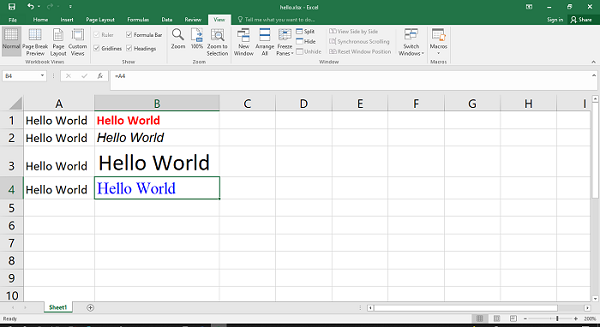
On the other hand, we can use the font_color, font_name and font_size attributes to format text as shown in the following example
import xlsxwriter
wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
ws = wb.add_worksheet()
for row in range(4):
ws.write(row,0, "Hello World")
f1=wb.add_format({'bold':True, 'font_color':'red'})
f2=wb.add_format({'italic':True,'font_name':'Arial'})
f3=wb.add_format({'font_size':20})
f4=wb.add_format({'font_color':'blue','font_size':14,'font_name':'Times New Roman'})
ws.write('B1', '=A1', f1)
ws.write('B2', '=A2', f2)
ws.write('B3', '=A3', f3)
ws.write('B4', '=A4', f4)
wb.close()
Output
The output of the above code can be verified by opening the worksheet in Excel.
Text Alignment
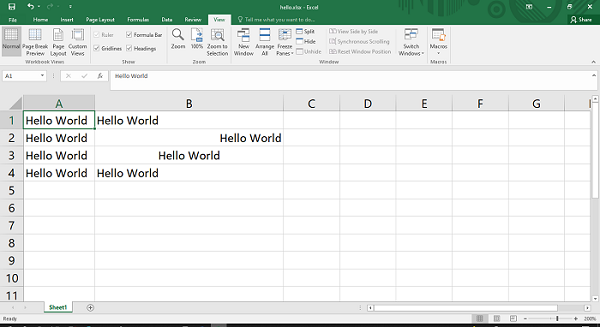
The XlsxWriter format object also allows for the creation of alignment methods/properties. The alignment property can have the values left, right, center, and align.
Example
import xlsxwriter
wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
ws = wb.add_worksheet()
for row in range(4):
ws.write(row,0, "Hello World")
ws.set_column('B:B', 30)
f1=wb.add_format({'align':'left'})
f2=wb.add_format({'align':'right'})
f3=wb.add_format({'align':'center'})
f4=wb.add_format({'align':'justify'})
ws.write('B1', '=A1', f1)
ws.write('B2', '=A2', f2)
ws.write('B3', '=A3', f3)
ws.write('B4', 'Hello World', f4)
wb.close()
Output
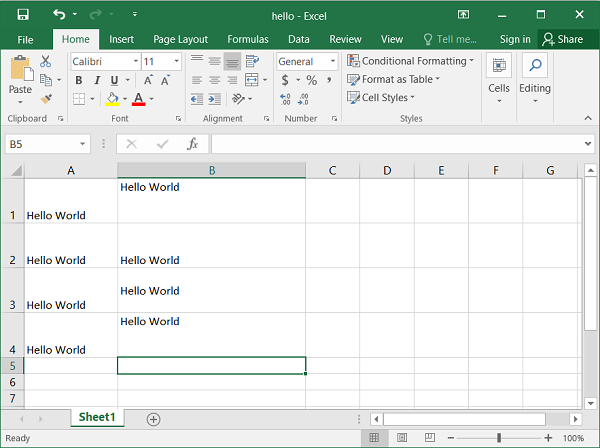
The output below shows the text “Hello World” with different alignments. Note that the width of column B is set to 30 using the set_column() method of the worksheet object.
Example
Format objects also have a valign attribute to control the vertical positioning of cells.
import xlsxwriter
wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
ws = wb.add_worksheet()
for row in range(4):
ws.write(row,0, "Hello World")
ws.set_column('B:B', 30)
for row in range(4):
ws.set_row(row, 40)
f1=wb.add_format({'valign':'top'})
f2=wb.add_format({'valign':'bottom'})
f3=wb.add_format({'align':'vcenter'})
f4=wb.add_format({'align':'vjustify'})
ws.write('B1', '=A1', f1)
ws.write('B2', '=A2', f2)
ws.write('B3', '=A3', f3)
ws.write('B4', '=A4', f4)
wb.close()
Output
In the above code, the set_row() method sets the height of rows 1 to 4 to 40.
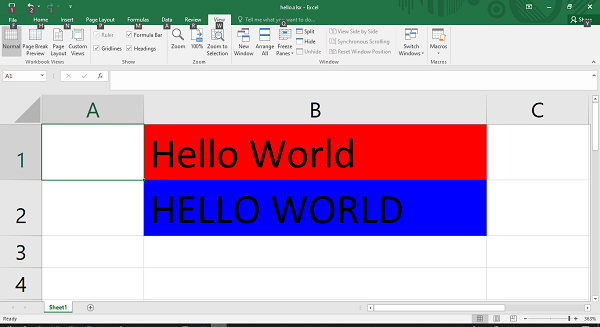
Cell Background and Foreground Colors
Two important attributes of the Format object are bg_color and fg_color, which are used to set the background and foreground colors of cells.
Example
import xlsxwriter
wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
ws = wb.add_worksheet()
ws.set_column('B:B', 30)
f1=wb.add_format({'bg_color':'red', 'font_size':20})
f2=wb.add_format({'bg_color':'#0000FF', 'font_size':20})
ws.write('B1', 'Hello World', f1)
ws.write('B2', 'HELLO WORLD', f2)
wb.close()
Output
The output of the above code looks like this: –