SciPy Ndimage
SciPy Ndimage
SciPy The ndimage submodule is dedicated to image processing. Here, ndimage refers to an n-dimensional image.
Some of the most common image processing tasks are as follows:
- Input/output, displaying images
- Basic operations – cropping, flipping, rotating, etc.
- Image filtering – denoising, sharpening, etc.
- Image Segmentation – Labeling pixels that correspond to different objects
- Classification
- Feature Extraction
- Registration
Let’s discuss how to use SciPy to implement some of these functions.
Opening and Writing Image Files
SciPy includes images in the misc package. We’ll use these images to learn about image manipulation. Let’s take a look at the following examples.
from scipy import misc
f = misc.face()
misc.imsave('face.png', f) # uses the Image module (PIL)
import </pre>
<p>The above program will produce the following output. </p>
<p><img alt="SciPy - Ndimage" decoding="async" src="https://static.deepinout.com/geekdocs/2023/03/20230323084307-1.jpg" title="SciPy - Ndimage"></p>
<p>Any image, in its raw form, is a combination of colors represented by numbers in a matrix format. Machines understand and manipulate images based solely on these numbers. RGB is a popular representation. </p>
<p>Let's look at the statistics of the above image. </p>
<pre><code class="language-python line-numbers">from scipy import misc
face = misc.face(gray = False)
print face.mean(), face.max(), face.min()
The above program will produce the following output.
110.16274388631184, 255, 0
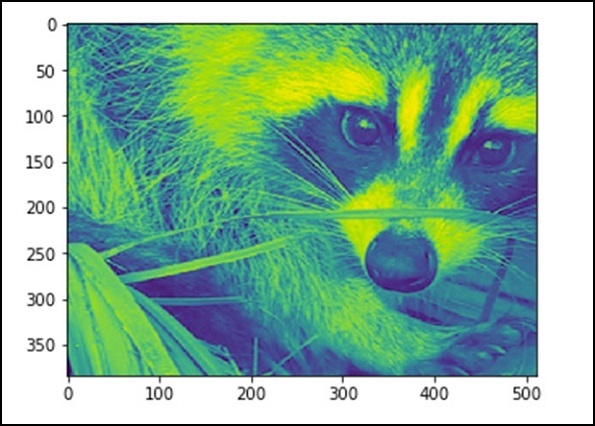
Now that we know that images are made up of numbers, any change in the numerical values will change the original image. Let’s perform some geometric transformations on the image. The basic geometric operation is cropping.
from scipy import misc
face = misc.face(gray = True)
lx, ly = face.shape
# Cropping
crop_face = face[lx / 4: - lx / 4, ly / 4: - ly / 4]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(crop_face)
plt.show()
The above program will produce the following output.
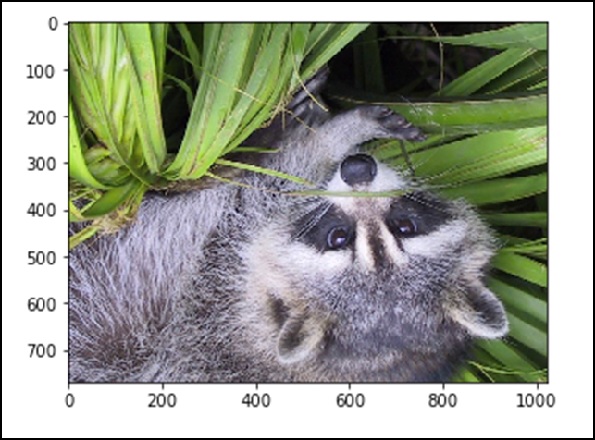
We can also perform some basic operations, such as flipping the image, as described below.
# flip up <-> down
from scipy import misc
face = misc.face()
flip_ud_face = np.flipud(face)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(flip_ud_face)
plt.show()
The above program will produce the following output.

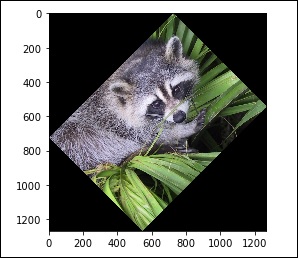
In addition, we have the rotate() function, which can rotate an image by a specified angle.
# rotation
from scipy import misc,ndimage
face = misc.face()
rotate_face = ndimage.rotate(face, 45)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(rotate_face)
plt.show()
The above program will produce the following output.
Filters
Let’s discuss how filters aid in image processing.
What is filtering in image processing?
Filtering is a technique for modifying or enhancing an image. For example, you can filter an image to emphasize certain features or remove others. Image processing operations performed using filtering include smoothing, sharpening, and edge enhancement.
Filtering is a neighborhood operation in which the value of any given pixel in the output image is determined by applying an algorithm to the values of the pixels in the neighborhood of the corresponding input pixel. Let’s perform some operations using SciPy ndimage.
Blurring
Blurring is widely used to reduce noise in images. We can also perform filtering operations to see the changes in the image. Let’s consider the following example.
from scipy import misc
face = misc.face()
blurred_face = ndimage.gaussian_filter(face, sigma=3)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(blurred_face)
plt.show()
The above program will produce the following output.
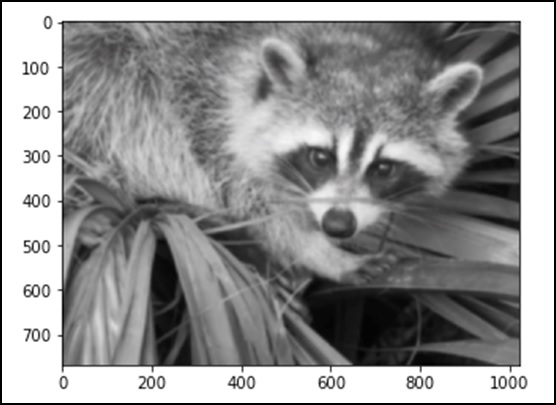

The sigma value represents the degree of blur, in units of 5. We can see how adjusting the sigma value affects image quality. For more details on blurring, please click on the →DIP (Digital Image Processing) Tutorial.
Edge Detection
Let’s discuss how edge detection aids image processing.
What is Edge Detection?
Edge detection is an image processing technique used to find the boundaries of objects in an image. It works by detecting discontinuities in brightness. Edge detection is used in image segmentation and data extraction in fields such as image processing, computer vision, and machine vision.
The most commonly used edge detection algorithms include
- Sobel
- Canny
- Prewitt
- Roberts
- Fuzzy Logic method
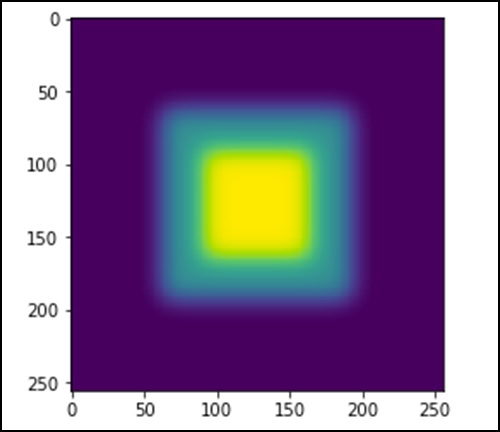
Let’s consider the following example.
import scipy.ndimage as nd
import numpy as np
im = np.zeros((256, 256))
im[64:-64, 64:-64] = 1
im[90:-90,90:-90] = 2
im = ndimage.gaussian_filter(im, 8)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()
The above program will produce the following output.
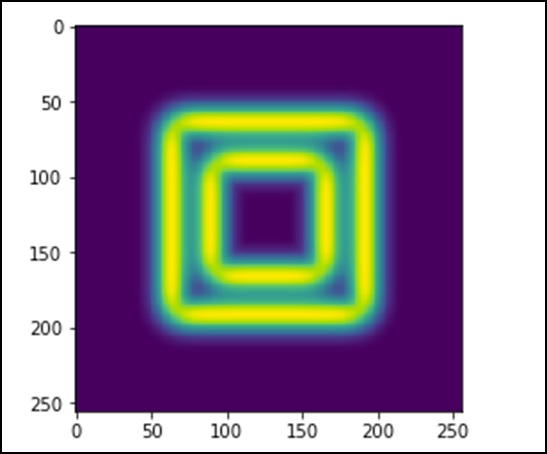
The image looks like a series of square blocks of color. Now, we will detect the edges of these blocks. ndimage provides a function called Sobel to perform this operation. NumPy provides the Hypot function to combine the two resulting matrices into one.
Let’s consider the following example.
import scipy.ndimage as nd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
im = np.zeros((256, 256))
im[64:-64, 64:-64] = 1
im[90:-90,90:-90] = 2
im = ndimage.gaussian_filter(im, 8)
sx = ndimage.sobel(im, axis = 0, mode = 'constant')
sy = ndimage.sobel(im, axis = 1, mode = 'constant')
sob = np.hypot(sx, sy)
plt.imshow(sob)
plt.show()
The above program will produce the following output.