What is relative position CSS
What is Relative Position in CSS
Reference: What is Position Relative CSS
Background
Relative positioning is a common positioning technique in CSS that allows you to position an element relative to its original position in the document flow. Relatively positioned elements still occupy space within the document flow but can be moved relative to their normal position using the top, bottom, left, and right properties.
A relatively positioned element is positioned relative to its parent element, or if no parent is specified, relative to the nearest ancestor element with a positioned property. This makes relative positioning a flexible layout tool, particularly useful for fine-tuning the position of an element or creating visual effects without affecting the layout of other elements.
The following is a simple example demonstrating how to use relative positioning CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Relative Positioning Example</title>
<style>
.container {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box {
position: relative;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
top: 50px;
left: 50px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:

In this example, the .box element is positioned relative to its parent element, .container, moving 50 pixels down and 50 pixels to the right. This use of relative positioning can help developers more precisely control page layout and element positioning.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Relative Position CSS Example</title>
<style>
/* Base styles for the container and items */
.container {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid #333;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.item {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: #f00;
position: absolute;
}
/* Specific position styles for each item */
.item-1 {
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
.item-2 {
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
.item-3 {
bottom: 20px;
right: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<!-- Three items with different relative positions -->
<div class="item item-1"></div>
<div class="item item-2"></div>
<div class="item item-3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:
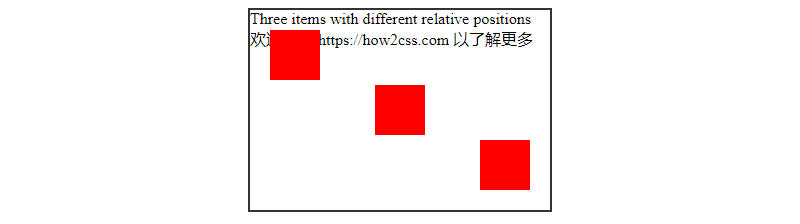
In this example, we create a container (.container) and three items (.item). The container has relative positioning, which means the items are positioned relative to the container rather than the document flow.
The items have absolute positioning and are positioned relative to their closest positioned ancestor. In this case, the container is the item’s closest positioned ancestor, so the items are positioned relative to the container.
.item-1 is offset 20 pixels from the container’s top-left corner to the bottom-right.
.item-2 is positioned horizontally and vertically in the container. top: 50%; left: 50%; is used to position the center of the item, and then transform: translate(-50%, -50%); is used to center it.
.item-3 is offset 20 pixels from the top left corner of the container relative to its bottom right corner.
This example demonstrates some basic use of relative positioning in CSS. By positioning elements relative to their container, you can easily create various layout and positioning effects.
Common Problems and Solutions
Question: What is Relative Positioning in CSS?
Relative positioning is a common positioning technique in CSS that allows us to position an element relative to its original position in the document flow without affecting the layout of other elements. Relative positioning is achieved using the position: relative; property.
Solution:
HTML structure:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Relative Positioning Example</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="box">
<p>This is a relative positioned box.</p>
</div> </div>
</body>
</html>
The effect of executing this code is as follows:
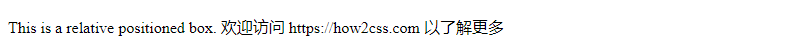
CSS style:
.container {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
position: relative; /* Set relative positioning to parent element */
}
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
position: relative; /* Sets relative positioning for child elements */
left: 20px; /* Offsets 20px to the right relative to the original position */
top: 20px; /* Offsets 20px to the bottom relative to the original position */
}
Explanation:
- In HTML, we have a container containing a box with text.
- Using CSS, we define styles for both the container and the box.
.containerclass sets a box with a fixed width and height and declaresposition: relative;, which means we want to position the elements within it relative to this box..boxclass represents the box we want to position relatively. Its position is controlled by theleftandtopproperties, which specify offsets relative to the original position.
The
The
Relative positioning allows us to fine-tune the position of an element without affecting the layout of other elements. This is particularly useful when creating complex layouts or implementing animation effects.
In practice, using CSS with relative positioning can provide developers with more flexible and maintainable layout solutions. By combining relatively positioned elements with other CSS properties, you can create responsive layouts that ensure consistency across different devices and screen sizes. Here’s a detailed example showing how to apply relative position CSS in a real-world project to create a simple responsive layout:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Relative Position CSS Example</title>
<style>
/* Reset some default styles */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
/* Define the container */
.container {
width: 100%;
max-width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: space-between;
}
/* Define the card style */
.card {
width: calc(33.33% - 20px); /* Ensure proper spacing between cards */
margin-bottom: 20px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
padding: 20px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
position: relative; /* Enable relative positioning */
}
/* Define the image style */
.card img {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
}
/* Define the overlay style */
.overlay {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
color: #fff;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
opacity: 0;
transition: opacity 0.3s ease;
}
/* Define the hover effect */
.card:hover .overlay {
opacity: 1;
}
/* Define the overlay content */
.overlay-content {
text-align: center;
}
/* Define the title style */
.title {
font-size: 20px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
/* Define the subtitle style */
.subtitle {
font-size: 16px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<!-- Card 1 -->
<div class="card">
<img src="https://coder-cafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/image1.jpg" alt="Image 1">
<div class="overlay">
<div class="overlay-content">
<h2 class="title">Card 1 Title</h2>
<p class="subtitle">Subtitle</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Card 2 -->
<div class="card">
<img src="https://coder-cafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/image2.jpg" alt="Image 2">
<div class="overlay">
<div class="overlay-content">
<h2 class="title">Card 2 Title</h2>
<p class="subtitle">Subtitle</p>
</div>
</div> </div>
<!-- Card 3 -->
<div class="card">
<img src="https://coder-cafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/image3.jpg" alt="Image 3">
<div class="overlay">
<div class="overlay-content">
<h2 class="title">Card 3 Title</h2>
<p class="subtitle">Subtitle</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
In this example, we create a responsive layout with three cards. Each card has an image and an overlay that reveals the title and subtitle on hover. By using relative positioning to control the position of the overlay, we ensure that the overlay appears correctly within its relatively positioned parent element. We also use flexbox layout to achieve equal heights and responsive alignment of the cards. This example demonstrates how to apply relatively positioned CSS in practice to create attractive and responsive layouts.
Conclusion
Relative positioning CSS provides powerful flexibility and control in web design. By using relative positioning, developers can more precisely define the position of elements within the document flow without relying on the layout of other elements in the document. This technique not only makes responsive design easier to implement, but also improves page accessibility and user experience. In practical applications, relative positioning CSS is often used to create adaptive layouts, implement animation effects, and resolve stacking context issues. Mastering relative positioning CSS allows developers to design and manage web layouts more flexibly, providing users with a smoother and more consistent user experience.